1、概况
必赢bwin线路检测中心3003航天制导导航与控制系的历史可追溯到1958年,为满足“两弹一星”工程惯性制导技术的需要,在钱学森先生的提议下,林士谔先生在我校创建了国内第一个航空陀螺与惯性导航专业,是当时中苏合作的重点建设项目之一。1975年改为必赢bwin线路检测中心3003第五研究室,即控制与陀螺惯导研究室。1981年,国务院首批批准成立“航空与惯性导航”学科博士点。1988年被批准为“惯性技术与导航设备”首批全国重点学科。1997年调整为“精密仪器及机械”二级学科,是国家“211工程”首批批准的重点建设单位。2005年正式更名为航天制导导航与控制系,隶属于国家一级学科“控制学科与工程”下的“导航、制导与控制”专业二级学科,“双一流”学科建设单位。
2、学科建设
航天制导导航与控制系所属“控制科学与工程”一级学科在国内最早拥有该一级学科博士学位点,一直是国家重点一级学科,全国排名靠前。本系所属二级学科为“导航、制导与控制”,拥有博士、硕士学位授予权,本科专业“探测制导与控制技术”入选2020年度国家级一流专业。航天制导导航与控制系是一个综合性的工程技术学科,涉及自动控制原理、电子、空气动力学、力学和机械等学科,研究涉及控制、导航、制导、仿真计算、信息处理与试验等众多领域。
3、师资队伍
航天制导导航与控制系现有固定教师16人,其中教授4人、副教授8人、讲师3人、实验室管理人员1人,15人拥有博士学位。我系教师长期以国家航天需求为牵引,形成了以兼职博导为指导、教授牵头和青年教师为骨干的教学和科研团队,是一支年富力强和富有创新意识的学术队伍。
4、教学工作
精品课程:自动控制原理B(双语),制导与控制原理
特色课程:惯性导航基础,GPS定位原理及应用,航天器控制(双语),天文基础与航天,航天器姿态测量与确定,航天器姿态控制系统设计,飞行控制技术,航天工程概论,天文导航技术基础,卡尔曼滤波基础,传感器技术与测试系统等。
5、科研工作
我系服务于航天器总体,开展针对各类航天器的系统级导航、制导与控制技术研究,主要研究方向为:
(1)自适应控制与智能控制理论与应用研究;
(2)航天器动力学与控制;
(3)高速飞行器制导与控制技术;
(4)混合系统理论及应用;
(5)自主导航及最优滤波技术等。
6、实验室建设
2007年建成航天制导导航与控制实验室,主要设备有:
1套三轴转台并配1套太阳模拟器;2套单轴转台;2套地球模拟器。
以转台为中心的实验室即为本专业本科生和研究生教学实验基础,又可以服务于相关科研实验。
7、教学、科研近五年标志性成果
教学(近五年):北航校级教学成果一等奖1项、二等奖4项、三等奖4项;“西飞”奖教金二等奖;北航“三育人”先进个人;北航“我爱我师”十佳教师。
科研(近五年):中国船舶重工集团公司科学技术三等奖1项;省部级科学技术进步三等奖1项;省部级科学技术进步奖和发明奖三等奖4项;出版专著译著6部(包括1部英文专著)、教材2部。
学术成果:在IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems、AIAAJournal、JournalofGuidanceDynamics&Control、Automatica、航空学报和宇航学报等国内外权威期刊和有关会议发表论文400余篇,其中SCI检索近100篇,EI检索近200篇;授权专利50项。
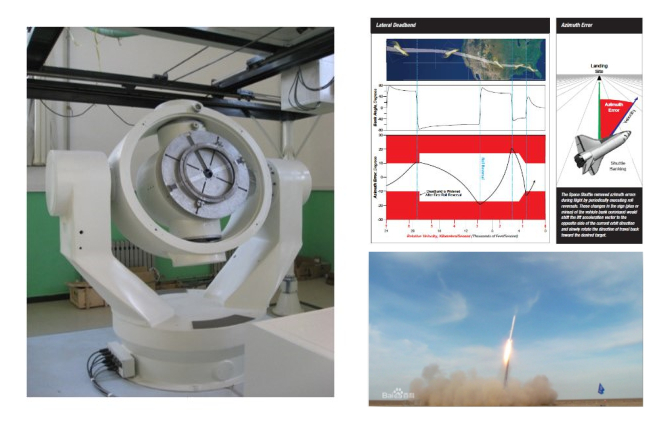
航天器飞行及再入控制
航天器飞行及再入控制主要包括自主任务决策、规划及飞行/再入控制算法等。着重研究通讯系统、航天器动力学及智能飞行控制技术间的互动关系,提升飞行控制系统的自主性;建立智能飞行控制算法验证平台,在半实物系统上验证智能算法的有效性。部分研究成果已成功应用于某型高空飞行器。
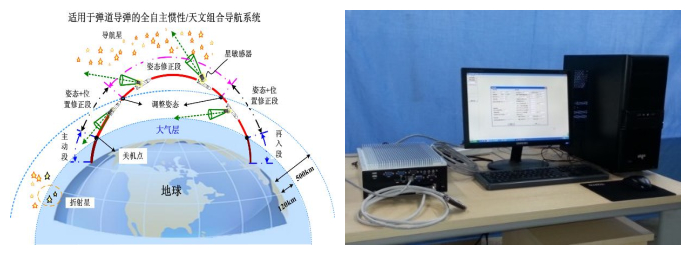
惯性/星敏感器自主组合导航系统
为了实现航天器自主飞行,提出了捷联惯性导航系统与星敏感器进行深层次组合的自主导航系统,惯导不仅用于星敏感器输出的姿态和基于星光折射的位置信息修正误差,也用于辅助星图动态拖尾补偿,提高其动态范围,并研制成功了动态实时电子注入式星图模拟器,具有科学级星像质心精度,进行星敏感器功能及精度测试,已应用于多家航天院所。
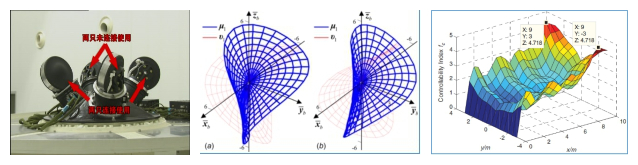
航天器先进姿态与振动控制
航天器先进姿态与振动控制方法包括航天器的欠驱动姿态控制、容错姿态控制与新概念(利用分布式角动量交换装置)振动控制方法。重点研究姿态控制系统故障模式下的智能控制策略与算法,提升航天器在轨运行的可靠性;同时研究新系统的动力学机理与控制方法,为工程应用提供新理论和新技术。

专著
Department ofAerospaceGuidance, Navigation,and Control
1、Overview
The history of department ofAerospace Guidance, Navigation, and Controlcan be traced up to 1958 when Prof. Lin Shie established the first aeronautics gyroscope and inertial navigation specialty of China for the project“TwoBombs andOneSatellite”. The specialty was one of the 122 key re-named asthe Fifth Research Lab (Control andGyroscopeInertialNavigation Research Lab) of Beihang University. In 1981, the first doctoral program of“Aeronautics andInertialNavigation”was authorized by the State Council of Chine. In1988, the first key discipline“InertialTechnology andNavigationEquipment”was authorized. In 1997, it had been regulated to secondary discipline“PrecisionInstruments andMachinery”and became the first one of the key departments of Project211. In 2005, it was re-named formally as“Department ofAerospaceGuidance,Navigation,andControl”, and belonged to the secondary discipline“Navigation,Guidance,andControl”under the first-degree priority discipline“ControlScience andEngineering”andsponsored by “Double First-Class” initiative. Currently, there are 14facultyand staffsin the department, including 3 professors and7associate professors. Besides, there are also 3adjunct professorsincluding2academicians of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and 1 academicians of the Chinese Academy of Engineering Sciences (CAES).
2、Discipline Construction
The first level discipline of the department is “Control Science and Engineering,” which is the national key first level discipline and has high rank over the country. The second level discipline of the department is “Navigation, Guidance, and Control,” in which master and doctor degrees are allowed to confer. Our undergraduate program “Detection, Guidance, and Control Techniques” has been qualified as the China first class major by the Ministry of Education in 2020. The major of aerospace guidance, navigation, and control is a comprehensive major of engineering technology, and consists of many disciplines such as automatic control, electronics, aerodynamics, mechanics and machinery. The research involves many fields including control, navigation, guidance, simulation, information processing and experiments, etc.
3、Faculty
The department ofaerospaceguidance,navigation,and control has 14 full-time teachers including 3 professors, 7 associate professors, 3 lecturers, and 1lab manager, and 12 of them hold doctoral degrees. The department also has three part-timePh. D advisors: CAES academician Huang Ruisong, CAS academician Wu Hongxin, and CAS academician Bao Weimin. The department has attracted a vigorous and innovative group of scholars such as full, associate, assistant and adjunct professors. They have long been conducting cutting-edge researches for the development of national aerospace industry.
4、Teaching
High-quality courses: Principle of automatic control B (Bilingual Curriculum), Principle of guidance and control
Specialty courses: Inertial navigation, Principle and application of GPS, Control of spacecraft (Bilingual Curriculum), Astronomy and space, Attitude measurement and determination of spacecraft, Attitude control system design for spacecraft, Flight control technique, Introduction of aerospace engineering, Astronavigation technique, Fundamentals of Kalman filter, Sensor technology and measurement system, etc.
5、Research Works
In the service of overall spacecraft, the department focuses on the subsystem research of navigation, guidance and control technique for spacecrafts.
The main research directions are:
Adaptive control and intelligent control theory and application
Aerospace dynamics and control
Hyper velocity vehicle guidance and control technique
Hybrid system theory and application
Autonomous Navigation and Optimal filtering technique
6、Laboratory Construction
In 2007, the aerospace GNC lab was established and belonged to theMinistry ofEducation key lab“Optimization design and dynamic simulation of spacecraft”. The mainfacilitiesinclude:
Three axis turntable and Sun simulator; Single axis turntable and Sun simulator; Single axis turntable; Earth simulator
Thefacilities can be used for undergraduate and graduate students’teaching and the science and technique researches.
7、Awards and Achievements
Teaching Awards (last 5 years) : The first prize of BUAA teaching award, 2009;The second prize of BUAA teaching award, 2009,2012, 2014, and 2016; The third prize of BUAA teaching award, 2009. The second prize of“Xi Fei”teaching award, 2010. BUAA‘San Yu Ren’advanced individual, 2010.BUAA‘My favorite teacher’, 2010.
Research Awards (last 5 years): The third prize of China Shipbuilding Industry Corp Science and Technology Award, 2008.Publishing 6 monographies and 2 books.
Academic Achievements: National Natural Science Foundation of China:15items. Published papers in the high-level academic magazines and proceedings:over400 (SCIindexed:100, EIindexed:200). Authorized national patent:50items.

Spacecraft flight and reentry control
The spacecraft flight and reentry control includes autonomous decision-making, planning, and flight control algorithms. In particular, we exploited the interaction between communication systems, spacecraft dynamics, and intelligent guidance technology to achieve high-level autonomy of the flight control systems. We developed an intelligent algorithm verification platform to verify the efficacy of the intelligent algorithms using hardware-in-the-loop simulation. Some algorithms have been verified by a spacecraft successfully.


Autonomous Integration of SINS/Star sensor
Aiming at the autonomous flight of spacecraft, the deep integration of a strap-down inertial navigation system (SINS) with a star sensor has been proposed. In the integration, not only do the attitude and the position by starlight refraction output by the star sensor compensate for the SINS error, but also the SINS output also aid the star image blur to improve the star sensor’s dynamic range. A dynamic star map simulator with the scientific-quality precision of star spot centroid has been developed successfully to test the function and accuracy of the star sensor for many aerospace institutes.

Advanced spacecraft attitude and vibration control
The advanced spacecraft attitude and vibration control includes under-actuated attitude control, fault tolerant attitude control and new concept vibration control (based on distributed angular momentum exchange devices). In particular, we exploited the intelligent control strategies and algorithms for the failure mode of attitude control systemtoimprove on-orbit reliability. We developed dynamical mechanisms and control methodologies for the new concept system to provide new theories and technologies for practical applications.

Books